Asian elephant
| Asian elephant Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|

| |
| A tusked bull Bandipur National Park, Karnataka, India | |

| |
| A cow, juveniles and a calf Yala National Park, Sri Lanka | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Proboscidea |
| Family: | Elephantidae |
| Genus: | Elephas |
| Species: | E. maximus[1]
|
| Binomial name | |
| Elephas maximus[1] | |
| Subspecies[1] | |
| |
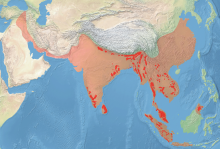
historical range
range in early 21st century
| |
The Asian elephant (Elephas maximus), also known as the Asiatic elephant, is a species of elephant distributed throughout the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia, from India in the west to Borneo in the east, and Nepal in the north to Sumatra in the south. Three subspecies are recognised—E. m. maximus, E. m. indicus and E. m. sumatranus. The Asian elephant is characterised by its long trunk with a single finger-like processing; large tusks in males; laterally folded large ears but smaller in contrast to African elephants; and wrinkled grey skin. The skin is smoother than African elephants and may be depigmented on the trunk, ears or neck. Adult males average 4 tonnes (4.4 short tons) in weight, and females 2.7 t (3.0 short tons).
It is one of only three living species of elephants or elephantids anywhere in the world, the others being the African bush elephant and African forest elephant. Further, the Asian elephant is the only living species of the genus Elephas. It is the second largest species of elephant after the African bush elephant. It frequently inhabits grasslands, tropical evergreen forests, semi-evergreen forests, moist deciduous forests, dry deciduous forests and dry thorn forests. They are herbivorous, eating about 150 kg (330 lb) of vegetation per day. Cows and calves form groups, while males remain solitary or form "bachelor groups" with other males. During the breeding season, males will temporarily join female groups to mate. Asian elephants have a large and well-developed neocortex of the brain, are highly intelligent and self-aware being able to display behaviors associated with grief, learning, greeting etc.
The Asian elephant is the largest living land animal in Asia. Since 1986, the Asian elephant has been listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List, as the population has declined by at least 50 per cent over the last three elephant generations, which is about 60–75 years. It is primarily threatened by loss of habitat, habitat degradation, fragmentation and poaching. Wild Asian elephants live to be about 60 years old. While female captive elephants are recorded to have lived beyond 60 years when kept in semi-natural surroundings, Asian elephants die at a much younger age in captivity; captive populations are declining due to a low birth and high death rate. The earliest indications of captive use of Asian elephants are engravings on seals of the Indus Valley civilisation dated to the 3rd millennium BC.
Taxonomy
Carl Linnaeus proposed the scientific name Elephas maximus in 1758 for an elephant from Ceylon.[4] Elephas indicus was proposed by Georges Cuvier in 1798, who described an elephant from India.[5] Coenraad Jacob Temminck named an elephant from Sumatra Elephas sumatranus in 1847.[6] Frederick Nutter Chasen classified all three as subspecies of the Asian elephant in 1940.[7] These three subspecies are currently recognised as valid taxa.[2][8] Results of phylogeographic and morphological analyses indicate that the Sri Lankan and Indian elephants are not distinct enough to warrant classification as separate subspecies.[9]
Three subspecies are recognised:[2][8]
- Sri Lankan elephant (E. maximus maximus Linnaeus, 1758)

- Indian elephant (E. maximus indicus Cuvier, 1798)

- Sumatran elephant (E. maximus sumatranus Temminck, 1847)

Sri Lankan elephants are the largest subspecies. Their skin colour is darker than of E. m. indicus and of E. m. sumatranus with larger and more distinct patches of depigmentation on ears, face, trunk and belly.[10] The skin color of the Indian elephant is generally grey and lighter than that of E. m. maximus but darker than that of E. m. sumatranus.[8]
A potential fourth subspecies, the Borneo elephant (Elephas maximus borneensis), occurs in Borneo's northeastern parts, primarily in Sabah (Malaysia), and sometimes in Kalimantan (Indonesia).[11] It was proposed by Paules Deraniyagala in 1950, who described an elephant in an illustration published in the National Geographic magazine, but not as a living elephant in accordance with the rules of the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature.[12][13] These elephants living in northern Borneo are smaller than all the other subspecies, but had larger ears, a longer tail, and straight tusks.[14] Results of genetic analysis indicate that their ancestors separated from the mainland population about 300,000 years ago.[15] A study in 2003, using mitochondrial DNA analysis and microsatellite data, indicated that the Borneo elephant population is derived from stock that originated in the region of the Sunda Islands, and suggests that the Borneo population has been separated from the other elephant populations of southeast Asia since the Pleistocene.[16]
The following Asian elephants were proposed as extinct subspecies, but are now considered synonymous with the Indian elephant:[8]
- Syrian elephant (E. m. asurus), proposed by Deraniyagala, based on fossil remains and Bronze Age illustrations.[17][18]
- Chinese elephant (E. m. rubridens), also proposed by Deraniyagala, based on a Chinese bronze statuette.[19]
- Javan elephant (E. m. sondaicus), also proposed by Deraniyagala, based on an illustration of a carving on the Buddhist monument of Borobudur.[20][13]
Evolution
The genus Elephas, of which the Asian elephant is the only living member, is the closest relative of the extinct mammoths. The two groups are estimated to have split from each other around 7 million years ago.[21] Elephas originated in Sub-Saharan Africa during the Pliocene and spread throughout Africa before expanding into the southern half of Asia.[22] The earliest Elephas species, Elephas ekorensis, is known from the Early Pliocene of East Africa, around 5–4.2 million years ago.[23] The oldest remains of the genus in Asia are known from the Siwalik Hills in the Indian subcontinent, dating to the late Pliocene, around 3.6-3.2 million years ago, assigned to the species Elephas planifrons.[24] The modern Asian elephant is suggested to have evolved from the species Elephas hysudricus, which first appeared at the beginning of the Early Pleistocene around 2.6 million years ago, and is primarily known from remains of Early-Middle Pleistocene age found on the Indian subcontinent.[25] Skeletal remains of E. m. asurus have been recorded from the Middle East: Iran, Iraq, Syria, and Turkey from periods dating between at least 1800 BC and likely 700 BC.[26]
| Elephantids phylogeny based on morphological and DNA evidence |
Description

In general, the Asian elephant is smaller than the African bush elephant and has the highest body point on the head. The back is convex or level. The ears are small with dorsal borders folded laterally. It has up to 20 pairs of ribs and 34 caudal vertebrae. The feet have five nail-like structures on each forefoot, and four on each hind foot.[8] The forehead has two hemispherical bulges, unlike the flat front of the African elephants.[27] Its long trunk or proboscis has only one fingerlike tip, in contrast to the African elephants which have two.[8] Hence, the Asian species relies more on wrapping around a food item and squeezing it into its mouth, rather than grasping with the tip. Asian elephants have more muscle coordination and can perform more complex tasks.[28]

Cows usually lack tusks; if tusks—in that case, called "tushes"—are present, they are barely visible and only seen when the mouth is open.[29] The enamel plates of the molars are greater in number and closer together in Asian elephants.[30] Some bulls may also lack tusks; these individuals are called "makhnas", and are especially common among the Sri Lankan elephant population.[31] A tusk from an 11 ft (3.4 m) tall elephant killed by Sir Victor Brooke measured 8 ft (2.4 m) in length, and nearly 17 in (43 cm) in circumference, and weighed 90 lb (41 kg). This tusk's weight is, however, exceeded by the weight of a shorter tusk of about 6 ft (1.8 m) in length which weighed 100 lb (45 kg), and there have reportedly been tusks weighing over 150 lb (68 kg).[32]

Skin colour is usually grey, and may be masked by soil because of dusting and wallowing. Their wrinkled skin is movable and contains many nerve centres. It is smoother than that of African elephants and may be depigmented on the trunk, ears, or neck. The epidermis and dermis of the body average 18 mm (0.71 in) thick; skin on the dorsum is 30 mm (1.2 in) thick providing protection against bites, bumps, and adverse weather. Its folds increase surface area for heat dissipation. They can tolerate cold better than excessive heat. Skin temperature varies from 24 to 32.9 °C (75.2 to 91.2 °F). Body temperature averages 35.9 °C (96.6 °F).[8]
Size
On average, when fully-grown, bulls are about 2.75 m (9.0 ft) tall at the shoulder and 4.0 t (4.4 short tons) in weight, while cows are smaller at about 2.40 m (7.9 ft) at the shoulder and 2.7 t (3.0 short tons) in weight.[33][34][35] Sexual dimorphism in body size is relatively less pronounced in Asian elephants than in African bush elephants; with bulls averaging 15% and 23% taller in the former and latter respectively.[33] Length of body and head including trunk is 5.5–6.5 m (18–21 ft) with the tail being 1.2–1.5 m (3.9–4.9 ft) long.[8] The largest bull elephant ever recorded was shot by the Maharajah of Susang in the Garo Hills of Assam, India, in 1924, it weighed an estimated 7 t (7.7 short tons), stood 3.43 m (11.3 ft) tall at the shoulder and was 8.06 m (26.4 ft) long from head to tail.[33][36][37] The Raja Gaj elephant of Bardia National Park was estimated to be 3.4 m (11.3 ft) tall at the shoulder and one of the biggest Asian bull elephant.[38][39][40] There are reports of larger individuals as tall as 3.7 m (12 ft).[32]


Distribution and habitat
Asian elephants are distributed throughout the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia, from India in the west, to Borneo in the east, and Nepal in the north, to Sumatra in the south.[2] They inhabit grasslands, tropical evergreen forests, semi-evergreen forests, moist deciduous forests, dry deciduous forests and dry thorn forests, in addition to cultivated and secondary forests and scrublands. Over this range of habitat types elephants occur from sea level to over 3,000 m (9,800 ft). In the eastern Himalaya in northeast India, they regularly move up above 3,000 m (9,800 ft) in summer at a few sites.[41]

In Bangladesh, some isolated populations survived in the south-east Chittagong Hills in the early 1990s.[42] In Malaysia's northern Johor and Terengganu National Park, two Asian elephants tracked using satellite tracking technology spent most of their time in secondary or "logged-over forest"; they travelled 75% of their time in an area less than 1.5 km (0.93 mi) away from a water source.[43] In China, the Asian elephant survives only in the prefectures of Xishuangbanna, Simao and Lincang of southern Yunnan. As of 2020[update], the estimated population was around 300 individuals.[44]
As of 2017, the estimated wild population in India account for nearly three-fourths of the extant population, at 27,312 individuals.[45] In 2019, the Asian elephant population in India increased to an estimated 27,000–29,000 individuals.[46][47] As of 2019[update], the global wild population was estimated at 48,323–51,680 individuals.[48]
Ecology and behaviour
Asian elephants are crepuscular.[8] They are classified as megaherbivores and consume up to 150 kg (330 lb) of plant matter per day.[49] Around 50 to 75% of the day is devoted to eating.[50] They are generalist feeders, and are both grazers and browsers. They are known to feed on at least 112 different plant species, most commonly of the order Malvales, as well as the legume, palm, sedge and true grass families.[51] They browse more in the dry season with bark constituting a major part of their diet in the cool part of that season.[52] They drink at least once a day and are never far from a permanent source of fresh water.[8] They need 80–200 litres of water a day and use even more for bathing. At times, they scrape the soil for clay or minerals.[53][54]


Cows and calves move about together as groups, while bulls disperse from their mothers upon reaching adolescence. Bulls are solitary or form temporary "bachelor groups".[55] Cow-calf units generally tend to be small, typically consisting of three adults (most likely related females) and their offspring.[56] Larger groups of as many as 15 adult females have also been recorded.[57] Seasonal aggregations of 17 individuals including calves and young adults have been observed in Sri Lanka's Uda Walawe National Park. Until recently, Asian elephants, like African elephants, were thought to be under the leadership of older adult females, or matriarchs. It is now recognized that cows form extensive and very fluid social networks, with varying degrees of associations between individuals.[58] Social ties generally tend to be weaker than in African bush elephants.[57] Unlike African elephants, which rarely use their forefeet for anything other than digging or scraping soil, Asian elephants are more agile at using their feet in conjunction with the trunk for manipulating objects. They can sometimes be known for their violent behavior.[27]

Asian elephants are recorded to make three basic sounds: growls, squeaks and snorts. Growls in their basic form are used for short distance communication. During mild arousal, growls resonate in the trunk and become rumbles while for long-distance communication, they escalate into roars. Low-frequency growls are infrasonic and made in many contexts. Squeaks come in two forms: chirpings and trumpets. Chirping consists of multiple short squeaks and signals conflict and nervousness. Trumpets are lengthened squeaks with increased loudness and are produced during extreme arousal. Snorts signal changes in activity and increase in loudness during mild or strong arousal. During the latter case, when an elephant bounces the tip of the trunk, it creates booms which serve as threat displays.[59] Elephants can distinguish low-amplitude sounds.[60]
Rarely, tigers have been recorded attacking and killing calves, especially if the calves become separated from their mothers, stranded from their herd, or orphaned. Adults are largely invulnerable to natural predation. There is a singular anecdotal case of a mother Asian elephant allegedly being killed alongside her calf; however, this account is contestable.[61][62] In 2011 and 2014, two instances were recorded of tigers successfully killing adult elephants; one by a single tiger in Jim Corbett National Park on a 20-year-old young adult elephant cow, and another on a 28-year-old sick adult bull in Kaziranga National Park further east, which was taken down and eaten by several tigers hunting cooperatively.[63][64] Elephants appear to distinguish between the growls of larger predators like tigers and smaller predators like leopards; they react to leopards less fearfully and more aggressively.[65]
Reproduction
Reproduction in Asian elephants can be attributed to the production and perception of signaling compounds called pheromones. These signals are transmitted through various bodily fluids. They are commonly released in urine but in males they are also found in special secretions from the temporal glands.[66] Once integrated and perceived, these signals provide the receiver with information about the reproductive status of the sender. If both parties are ready to breed, reproductive ritualic behavior occurs and the process of sexual reproduction proceeds.[67]
Bulls will fight one another to get access to oestrus cows. Strong fights over access to females are extremely rare. Bulls reach sexual maturity around the age of 12–15. Between the ages of 10 and 20 years, bulls undergo an annual phenomenon known as "musth". This is a period where the testosterone level is up to 100 times greater than non-musth periods, and they become aggressive. Secretions containing pheromones occur during this period, from the paired temporal glands located on the head between the lateral edge of the eye and the base of the ear.[68] The aggressive behaviors observed during musth can be attributed to varying amounts of frontalin (1,5-dimethyl-6,8-dioxabicyclo[3.2.1]octane) throughout the maturation process of bulls. Frontalin is a pheromone that was first isolated in bark beetles but can also be produced in the bulls of both Asian and African Elephants. The compound can be excreted through urine as well as through the temporal glands of the bull, allowing signaling to occur. During musth, increased concentrations of frontalin in the bull's urine communicate the reproductive status of the bull to female elephants.[69]


Similar to other mammals, hormone secretion in female elephants is regulated by an estrous cycle. This cycle is regulated by surges in Luteinizing hormone that are observed three weeks from each other. This type of estrous cycle has also been observed in African Elephants but is not known to affect other mammals. The first surge in Luteinizing hormone is not followed by the release of an egg from the ovaries.[70] However, some female elephants still exhibit the expected mating protocols during this surge. Female elephants give ovulatory cues by utilizing sex pheromones. A principal component thereof, (Z)-7-dodecen-1-yl acetate, has also been found to be a sex pheromone in numerous species of insects.[71][72] In both insects and elephants, this chemical compound is used as an attractant to assist the mating process. In elephants, the chemical is secreted through urination and this aids in the attraction of bulls to mate. Once detected, the chemical stimulates the vomeronasal organ of the bull, thus providing information on the maturity of the female.[73]
Reproductive signaling exchange between male and female elephants are transmitted through olfactory cues in bodily fluids.[67] In males, the increase in frontalin during musth heightens their sensitivity to the (Z)-7-dodecen-1-yl acetate produced by female elephants.[69] Once perceived by receptors in the trunk, a sequence of ritualistic behaviors follow. The responses in males vary based on both the stage of development and the temperament of the elephant.[67] This process of receiving and processing signals through the trunk is referred to as flehmen. The difference in body movements give cues to gauge if the male is interested in breeding with the female that produced the secretion.[74] A bull that is ready to breed will move closer to the urine and in some cases an erection response is elicited. A bull that is not ready to breed will be timid and try to dissociate themselves from the signal.[67] In addition to reproductive communication, chemosensory signaling is used to facilitate same-sex interactions. When less developed males detect pheromones from a male in musth, they often retreat to avoid coming in contact with aggressive behaviors. Female elephants have also been seen to communicate with each other through pheromone in urine.[67] The purpose of this type of intersex communication is still being investigated. However, there are clear differences in signaling strength and receiver response throughout different stages of the estrous cycle.[74]

The gestation period is 18–22 months, and the cow gives birth to one calf, only occasionally twins. The calf is fully developed by the 19th month, but stays in the womb to grow so that it can reach its mother to feed. At birth, the calf weighs about 100 kg (220 lb), and is suckled for up to three years. Once a female gives birth, she usually does not breed again until the first calf is weaned, resulting in a four to five-year birth interval.[75][76] During this period, mother to calf communication primarily takes place through temporal means. However, male calves have been known to develop sex pheromone-producing organs at a young age. Early maturity of the vomeronasal organ allows immature elephants to produce and receive pheromones.[77] It is unlikely that the integration of these pheromones will result in a flehmen response in a calf.[74] Females stay on with the herd, but mature males are chased away.[78]

Female Asian elephants sexually mature around the age of 10~15 and keep growing until 30, while males fully mature at more than the age of 25, and constantly grow throughout their life.[79][80] Average elephant life expectancy is approximately 60 years.[8] Some individuals are known to have lived into their late 80s.[81] Generation length of the Asian elephant is 22 years.[82]
Intelligence
Asian elephants have a very large and highly developed neocortex, a trait also shared by humans, apes and certain dolphin species. They have a greater volume of cerebral cortex available for cognitive processing than all other existing land animals. Results of studies indicate that Asian elephants have cognitive abilities for tool use and tool-making similar to great apes.[83] They exhibit a wide variety of behaviours, including those associated with grief, learning, allomothering, mimicry, play, altruism, use of tools, compassion, cooperation, self-awareness, memory, and language.[84] Elephants reportedly head to safer ground during natural disasters like tsunamis and earthquakes, but data from two satellite-collared Sri Lankan elephants indicate this may be untrue.[85] Several students of elephant cognition and neuroanatomy are convinced that Asian elephants are highly intelligent and self-aware.[86][87][88] Others contest this view.[89][90]
Threats
The pre-eminent threats to the Asian elephant today are the loss, degradation and fragmentation of its habitat, which leads to increasing conflicts between humans and elephants. Asian elephants are poached for ivory and a variety of other products including meat and leather.[2] The demand for elephant skin has risen due to it being an increasingly-common ingredient in traditional Chinese medicine.[91][92]
Human–elephant conflict


In some parts of Asia, people and elephants have co-existed for thousands of years.[93] In other areas, people and elephants come into conflict, resulting in violence, and ultimately, the displacement of elephants.[94] The main causes of human-elephant conflict includes the growing human population, large-scale development projects and poor top-down governance. Proximate causes includes habitat loss due to deforestation, disruption of elephant migratory routes, expansion of agriculture and illegal encroachment into protected areas.[95]
Destruction of forests through logging, encroachment, slash-and-burn, shifting cultivation, and monoculture tree plantations are major threats to the survival of elephants. Human–elephant conflicts occur when elephants raid crops of shifting cultivators in fields, which are scattered over a large area interspersed with forests. Depredation in human settlements is another major area of human–elephant conflict occurring in small forest pockets, encroachments into elephant habitat, and on elephant migration routes.[96] However, studies in Sri Lanka indicate that traditional slash-and-burn agriculture may create optimal habitats for elephants by creating a mosaic of successional-stage vegetation. Populations inhabiting small habitat fragments are much more liable to come into conflict with humans.[97]
Development such as border fencing along the India–Bangladesh border has become a major impediment to the free movement of elephants.[98] In Assam, more than 1,150 humans and 370 elephants died as a result of human-elephant conflict between 1980 and 2003.[96] In a 2010 study, it was estimated that in India alone, over 400 people were killed by elephants each year, and 0.8 to 1 million hectares were damaged, affecting at least 500,000 families across the country.[99][100][101] Moreover, elephants are known to destroy crops worth up to US$2–3 million annually.[102] This has major impacts on the welfare and livelihoods of local communities, as well as the future conservation of this species.[95] In countries like Bangladesh and Sri Lanka, the Asian elephant is one of the most feared wild animals, even though they are less deadly than other local animals such as venomous snakes (which were estimated to claim more than 30 times more lives in Sri Lanka than elephants).[103][104]
As a whole, Asian elephants display highly sophisticated and sometimes unpredictable behaviour. Most untamed elephants try to avoid humans, but if they are caught off guard by any perceived physical threat, including humans, they will likely charge. This is especially true of males in musth and of females with young. Gunfire and other similar methods of deterring, which are known to be effective against many kinds of wild animals including tigers, may or may not work with elephants, and can even worsen the situation. Elephants that have been abused by humans in the past often become "rogue elephants", which regularly attack people with no provocation.[105][106][107]
Poaching
For ivory
The demand for ivory during the 1970s and 1980s, particularly in East Asia, led to rampant poaching and the serious decline of elephants in both Africa and Asia. In Thailand, the illegal trade in live elephants and ivory still flourishes. Although the amount of ivory being openly sold has decreased substantially since 2001, Thailand still has one of the largest and most active black markets for ivory seen anywhere in the world. Tusks from Thai-poached elephants also enter the market; between 1992 and 1997 at least 24 male elephants were killed for their tusks.[108]
Up to the early 1990s, Vietnamese ivory craftsmen used exclusively Asian elephant ivory from Vietnam and neighbouring Lao and Cambodia. Before 1990, there were few tourists and the low demand for worked ivory could be supplied by domestic elephants. Economic liberalisation and an increase in tourism raised both local and visitors' demands for worked ivory, which resulted in heavy poaching.[109]
For skin
The skin of the Asian elephant is used as an ingredient in Chinese medicine as well as in the manufacture of ornamental beads. The practice has been aided by China's State Forestry Administration (SFA), which has issued licences for the manufacture and sale of pharmaceutical products containing elephant skin, thereby making trading legal. In 2010, four skinned elephants were found in a forest in Myanmar; 26 elephants were killed by poachers in 2013 and 61 in 2016. According to the NGO Elephant Family, Myanmar is the main source of elephant skin, where a poaching crisis has developed rapidly since 2010.[110]
Disease
The elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus (EEHV) is a member of the Proboscivirus genus, a novel clade most closely related to the mammalian betaherpesviruses. As of 2011, it is responsible for as many as 70 deaths of both zoo and wild Asian elephants worldwide, especially in young calves.[111][112] In particular, several incidents of calves dying from elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus have been recorded in Myanmar.[113] The elephant schistosome is a parasitic trematode that uses the Asian elephant as a definitive host. Two other hosts may be the Indian elephant and the greater one-horned rhinoceros.[114]
Conservation
The Asian elephant is listed on CITES Appendix I.[3] It is a quintessential flagship species, deployed to catalyze a range of conservation goals, including habitat conservation at landscape scales, generating public awareness on conservation issues, and mobilisation as a popular cultural icon both in India and the West.[115][116][95] A key aspect of conservation is connectivity of the preferred movement routes of Asian elephants through areas with high vegetation cover and low human population density.[117]
The World Elephant Day is celebrated annually on 12 August since 2012. Events are organized to divulge information and to engage people about the problems that the Asian elephant is facing.[118] August has been established as the Asian Elephant Awareness Month by zoos and conservation partners in the United States.[119]
Karnataka state in India hosts the most Asian elephants of any known area, comprising around 20% of the total population in the country. The distribution of elephants in the state according to one estimate is roughly 38,310 km2 (14,790 sq mi).[120] In a 2013 study, an estimated 10, 000 elephants inhabited the Western Ghats, and were primarily threatened by poaching and habitat fragmentation. An increase in conflict with humans was also cited as a likely issue. Conservation plans aimed to establish wildlife corridors, stop poaching of bulls, and protect or manage land area.[121] Project Elephant was initiated in 1992 as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change of the Government of India. The project was initiated to protect the Indian elephant and its habitats and to establish dedicated elephant reserves for sustaining elephant populations.[122]
The distribution of elephants in Sri Lanka is only two-fifths of what it was in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Due to this decrease, interactions with humans occur much more frequently. During a 2003 survey, the local people expressed some form of disapproval towards the conservation of Asian elephants as farmers viewed them as pests, however, most of the participants were supportive of the idea.[123]
In China, Asian elephants are under first-level protection. Yunnan province has 11 national and regional nature reserves. In total, the covered protected area in China is about 510,000 ha (1,300,000 acres). In 2020, the population of Asian elephants in Yunnan was estimated at around 300 individuals. As conflicts between humans and wild elephants have emerged around protected areas in the last years, the prefecture of Xishuangbanna built food bases and planted bananas and bamboo to create a better habitat.[44]
In Thailand, Salakpra Wildlife Sanctuary and Tham Than Lot National Park are protected areas hosting around 250–300 elephants, according to figures from 2013[update].[124] In recent years the National Park has faced issues due to encroachment and over-exploitation.[125] In India, the National Board of Wildlife recommended to allow coal mining in Dehing Patkai National Park in April 2020. The decision raised concerns between students and environmental activists who launched an online campaign to stop the project.[126]
In captivity

About half of the global zoo elephant population is kept in European zoos, where they have less than half (18.9 years) the median life span of conspecifics (41.6 years) in protected populations in range countries. This discrepancy is clearest in Asian elephants: infant mortality is more than two to three times that seen in Burmese timber camps, and adult survivorship in zoos has not improved significantly in recent years. One risk factor for Asian zoo elephants is being moved between institutions, with early removal from the mother tending to have additional adverse effects. Another risk factor is being born into a zoo rather than being imported from the wild, with poor adult survivorship in zoo-born Asians apparently being conferred prenatally or in early infancy. Likely causes for compromised survivorship is stress and/or obesity.[127] Foot problems are commonly observed in captive elephants. These are related to lack of exercise, long hours standing on hard substrates, and contamination resulting from standing in their dung. Many of these problems are treatable. However, mistreatment may lead to serious disability or death.[128]
Demographic analysis of captive Asian elephants in North America indicates that the population is not self-sustaining. First year mortality is nearly 30 per cent, and fecundity is extremely low throughout the prime reproductive years.[129] Data from North American and European regional studbooks from 1962 to 2006 were analysed for deviations in the birth and juvenile death sex ratios. Of 349 captive calves born, 142 died prematurely. They died within one month of birth, major causes being stillbirth and infanticide by either the calf's mother or by one of the exhibition mates. The sex ratio of stillbirths in Europe was found to have a tendency for excess of males.[130]
Handling methods
Young elephants are captured from the wild and illegally imported to Thailand from Myanmar for use in the tourism industry; calves are used mainly in amusement parks and are trained to perform various stunts for tourists.[108] The calves are often subjected to a 'breaking in' process, which may involve being tied up, confined, starved, beaten and tortured; as a result, two-thirds may perish.[131] Handlers use a technique known as the training crush, in which "handlers use sleep-deprivation, hunger, and thirst to "break" the elephants' spirit and make them submissive to their owners"; moreover, handlers drive nails into the elephants' ears and feet.[132]
In culture

The Asian elephant is the national animal of Thailand and Laos.[133][134] It has also been declared as the national heritage animal of India.[135] Bones of Asian elephants excavated at Mohenjo-daro in the Indus Valley indicate that they were tamed in the Indus Valley Civilisation and used for work. Decorated elephants are also depicted on seals and were modelled in clay.[136] The Asian elephant became a siege engine, a mount in war, a status symbol, a beast of burden, and an elevated platform for hunting during historical times in South Asia.[137]

Asian elephants have been captured from the wild and tamed for use by humans. Their ability to work under instruction makes them particularly useful for carrying heavy objects. They have been used particularly for timber-carrying in jungle areas. Other than their work use, they have been used in war, in ceremonies, and for carriage.[138] It is reported that war elephants are still used by the Kachin Independence Army (KIA) in Kachin State in northern Myanmar against Myanmar's military. The KIA use about four dozen elephants to carry supplies.[139]
The Asian elephant plays an important part in the culture of the subcontinent and beyond, being featured prominently in the Panchatantra fables and the Buddhist Jataka tales. They play a major role in Hinduism: the god Ganesha's head is that of an elephant, and the "blessings" of a temple elephant are highly valued. Elephants are frequently used in processions where the animals are adorned with festive outfits.[140]
The Asian elephant is depicted in several Indian manuscripts and treatises with notable amongst these including Matanga Lila (elephant sport) of Nilakantha.[140] The manuscript Hastividyarnava is from Assam in northeast India.[141] In the Burmese, Thai and Sinhalese animal and planetary zodiac, the Asian elephant, both tusked and tuskless, are the fourth and fifth animal zodiacs of the Burmese, the fourth animal zodiac of the Thai, and the second animal zodiac of the Sinhalese people of Sri Lanka.[142][143] Similarly, the elephant is the twelfth animal zodiac in the Dai animal zodiac of the Dai people in southern China.[144]
See also
References
- ^ a b Shoshani, J. (2005). "Species Elephas maximus". In Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 90. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- ^ a b c d e Williams, C.; Tiwari, S.K.; Goswami, V.R.; de Silva, S.; Kumar, A.; Baskaran, N.; Yoganand, K. & Menon, V. (2020). "Elephas maximus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T7140A45818198. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T7140A45818198.en. Retrieved 15 January 2022.
- ^ a b "Appendices". Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES). Archived from the original on 5 December 2017. Retrieved 6 June 2022.
- ^ Linnaei, C. (1758). "Bruta". Caroli Linnæi Systema naturæ per regna tria naturæ, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis. Vol. Tomus I. Holmiae: Impensis Direct. Laurentti Salvii. p. 33.
- ^ Cuvier, G. (1798). "Elephas indicus". Tableau elementaire de l'histoire naturelle des animaux. Paris: Baudouin. pp. 148–149.
- ^ Temminck, C. J. (1847). "Elephas sumatranus". Coup-d'oeil général sur les possessions néerlandaises dans l'Inde archipélagique. Vol. Tome second. Leide: A. Arnz and Comp. p. 91.
- ^ Chasen, F.N. (1940). "A handlist of Malaysian mammals, a systematic list of the mammals of the Malay Peninsula, Sumatra, Borneo and Java, including the adjacent small islands" (PDF). Bulletin of the Raffles Museum. 15: 1–209. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 February 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Shoshani, J.; Eisenberg, J. F. (1982). "Elephas maximus" (PDF). Mammalian Species (182): 1–8. doi:10.2307/3504045. JSTOR 3504045. Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 April 2013.
- ^ Fleischer, R.C.; Perry, E.A.; Muralidharan, K.; Stevens, E.E. & Wemmer, C.M. (2001). "Phylogeography of the Asian elephant (Elephas maximus) based on mitochondrial DNA". Evolution. 55 (9): 1882–1892. doi:10.1111/j.0014-3820.2001.tb00837.x. JSTOR 2680432. PMID 11681743.
- ^ Shoshani, J. (2006). "Taxonomy, Classification, and Evolution of Elephants". In Fowler, M. E.; Mikota, S. K. (eds.). Biology, medicine, and surgery of elephants. Wiley-Blackwell. pp. 3–14. ISBN 0813806763. Archived from the original on 20 October 2022. Retrieved 4 June 2020.
- ^ Farrows. "Bornean Elephant: Species in World Land Trust reserves". World Land Trust. Archived from the original on 14 May 2021. Retrieved 26 January 2021.
- ^ Deraniyagala 1955, p. 123–124.
- ^ a b Cranbrook, E.; Payne, J. & Leh, C.M.U. (2007). "Origin of the elephants Elephas maximus L. of Borneo" (PDF). Sarawak Museum Journal. 63: 95–125. Archived (PDF) from the original on 27 September 2012. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
- ^ Nurzhafarina, O.; Maryati, M.; Ahmad, A.H.; Nathan, S.; Pierson, H.T.; Goosens, B. (2008). "A preliminary study on the morphometrics of the Bornean Elephant" (PDF). Journal of Tropical Biology and Conservation. 4 (1): 109–113. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 March 2012.
- ^ Fernando, P.; Vidya, T. N. C.; Payne, J.; Stuewe, M.; Davison, G.; Alfred, R. J.; Andau, P.; Bosi, E. & Kilbourn, A. (2003). "DNA Analysis Indicates That Asian Elephants Are Native to Borneo and Are Therefore a High Priority for Conservation". PLOS Biology. 1 (1): e6. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0000006. PMC 176546. PMID 12929206.
- ^ Fernando, P.; Vidya T.N.C.; Payne J.; Stuewe M.; Davison G.; Alfred, R.J.; Andau, P.; Bosi, E.; Kilbourn, A.; Melnick, D.J. (2003). "DNA Analysis indicates that Asian Elephants are native to Borneo and are therefore a High Priority for conservation". PLOS Biology. 1 (1): e6. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0000006. PMC 176546. PMID 12929206.
- ^ Deraniyagala 1955, p. 116.
- ^ Girdland Flink, E.L.; Albayrak, E. & Lister, A. (2018). "Genetic insight into an extinct population of Asian elephants (Elephas maximus) in the Near East". Open Quaternary. 4 (1): 1–9. doi:10.5334/oq.36. hdl:2164/13525.
- ^ Deraniyagala 1955, p. 125.
- ^ Deraniyagala 1955, p. 124.
- ^ Rohland, Nadin; Reich, David; Mallick, Swapan; Meyer, Matthias; Green, Richard E.; Georgiadis, Nicholas J.; Roca, Alfred L.; Hofreiter, Michael (21 December 2010). "Genomic DNA Sequences from Mastodon and Woolly Mammoth Reveal Deep Speciation of Forest and Savanna Elephants". PLOS Biology. 8 (12): e1000564. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1000564. ISSN 1545-7885. PMC 3006346. PMID 21203580.
- ^ Haynes, G. (1993). Mammoths, Mastodonts, and Elephants: Biology, Behavior and the Fossil Record. Cambridge University Press. p. 8. ISBN 978-0521456913. Archived from the original on 17 March 2024. Retrieved 19 March 2018.
- ^ Sanders, William J.; Haile-Selassie, Yohannes (June 2012). "A New Assemblage of Mid-Pliocene Proboscideans from the Woranso-Mille Area, Afar Region, Ethiopia: Taxonomic, Evolutionary, and Paleoecological Considerations". Journal of Mammalian Evolution. 19 (2): 105–128. doi:10.1007/s10914-011-9181-y. ISSN 1064-7554. S2CID 254703858. Archived from the original on 17 March 2024. Retrieved 12 August 2023.
- ^ Iannucci, Alessio; Sardella, Raffaele (28 February 2023). "What Does the "Elephant-Equus" Event Mean Today? Reflections on Mammal Dispersal Events around the Pliocene-Pleistocene Boundary and the Flexible Ambiguity of Biochronology". Quaternary. 6 (1): 16. doi:10.3390/quat6010016. hdl:11573/1680082. ISSN 2571-550X.
- ^ Lister, Adrian M.; Dirks, Wendy; Assaf, Amnon; Chazan, Michael; Goldberg, Paul; Applbaum, Yaakov H.; Greenbaum, Nathalie; Horwitz, Liora Kolska (September 2013). "New fossil remains of Elephas from the southern Levant: Implications for the evolutionary history of the Asian elephant". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. 386: 119–130. Bibcode:2013PPP...386..119L. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2013.05.013. Archived from the original on 2 January 2023. Retrieved 12 August 2023.
- ^ Çakırlar, Canan; Ikram, Salima (3 May 2016). "'When elephants battle, the grass suffers.' Power, ivory and the Syrian elephant". Levant. 48 (2): 167–183. doi:10.1080/00758914.2016.1198068. ISSN 0075-8914.
- ^ a b Clutton-Brock, Juliet (1987). A Natural History of Domesticated Mammals. Cambridge University Press. p. 141. ISBN 978-0-292-71532-5.
- ^ Shoshani, J., ed. (2000). Elephants: Majestic Creatures of the Wild. Checkmark Books. pp. 38–41, 74–77. ISBN 978-0-87596-143-9. OCLC 475147472.
- ^ Chelliah, Karpagam; Sukumar, Raman (1 December 2013). "The role of tusks, musth and body size in male–male competition among Asian elephants, Elephas maximus". Animal Behaviour. 86 (6): 1207–1214. doi:10.1016/j.anbehav.2013.09.022. ISSN 0003-3472. Archived from the original on 2 December 2018. Retrieved 17 March 2024.
- ^ Nancy E. Todd (January 2010). "Qualitative Comparison of the Cranio-Dental Osteology of the Extant Elephants, Elephas Maximus (Asian Elephant) and Loxodonta africana (African Elephant)". Anatomical Record. 293 (1): 62–73. doi:10.1002/ar.21011. PMID 19937635. Archived from the original on 21 May 2024. Retrieved 21 May 2024.
- ^ "Makhna". Elephant database. Archived from the original on 21 May 2024. Retrieved 1 December 2023.
- ^ a b Lydekker, R. (1894). The Royal Natural History. Vol. 2. London: Frederick Warne and Co. pp. 522–523.
- ^ a b c Larramendi, A. (2016). "Shoulder height, body mass and shape of proboscideans". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 61 (3): 537–574. doi:10.4202/app.00136.2014.
- ^ Sukumar, R.; Joshi, N.V.; Krishnamurthy, V. (1988). "Growth in the Asian elephant". Proceedings: Animal Sciences. 97 (6): 561–571. doi:10.1007/BF03179558. S2CID 84871322.
- ^ Kurt, F.; Kumarasinghe, J.C. (1998). "Remarks on body growth and phenotypes in Asian elephant Elephas maximus". Acta Theriologica. 5 (Supplement): 135–153. doi:10.4098/AT.arch.98-39.
- ^ Pillai, N.G. (1941). "On the height and age of an elephant". Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society. 42: 927–928.
- ^ Wood, G. (1983). The Guinness Book of Animal Facts and Feats. Enfield, Middlesex: Guinness Superlatives. p. 17. ISBN 978-0-85112-235-9.
- ^ Furaha tenVelde, P. (1997). "The wild elephants of the Royal Bardia National Park, Nepal" (PDF). Gajah: Journal of the SSC Asian Elephant Specialist Group (17): 41–44.
- ^ Ben S. Roesch. "Living Stegodont or Genetic Freak?". Archived from the original on 8 November 2006. Retrieved 4 December 2024.
- ^ World's Largest Asian Elephant May Be Dead
- ^ Choudhury, A. U. (1999). "Status and conservation of the Asian elephant Elephas maximus in north-eastern India". Mammal Review. 29 (3): 141–173. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2907.1999.00045.x.
- ^ Sukumar, R. (1993). The Asian Elephant: Ecology and Management (Second ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 18. ISBN 978-0-521-43758-5. Archived from the original on 17 March 2024. Retrieved 15 December 2015.
- ^ Aini, S.; Sood, A. M.; Saaban, S. "Analysing elephant habitat parameters using GIS, remote sensing and analytic hierarchy process in Peninsular Malaysia". Pertanika Journal of Science & Technology. 23 (1): 37–50. Archived from the original on 17 May 2023. Retrieved 17 May 2023.
- ^ a b Shuang, F. (2020). "Solving a dilemma caused by elephants". ECNS. Archived from the original on 13 January 2021. Retrieved 6 September 2020.
- ^ "India has 27,312 elephants, census shows". The Hindu. 16 August 2017. Archived from the original on 3 December 2023. Retrieved 1 December 2023.
- ^ Srinivasaiah, Nishant M.; Vaidyanathan, Srinivas; Sukumar, Raman; Sinha, Anindya (2019). "Elephants on the Move: Implications for Human–Elephant Interaction". India International Centre Quarterly. 46 (3/4): 100–113. ISSN 0376-9771. JSTOR 26946286. Archived from the original on 21 May 2024. Retrieved 21 May 2024.
- ^ Baskaran, N.; Varma, S.; Sar, C.K.; Sukumar, R. (2011). "Current status of elephants in India". Gajah. 35: 47–54. Archived from the original on 21 May 2024. Retrieved 29 March 2024.
- ^ Menon, V.; Tiwari, S. (2019). "Population status of Asian elephants Elephas maximus and key threats". International Zoo Yearbook. 53 (1): 17–30. doi:10.1111/izy.12247. S2CID 209571148.
- ^ Samansiri, K. A. P.; Weerakoon, D. K. (2007). "Feeding Behaviour of Asian Elephants in the Northwestern Region of Sri Lanka" (PDF). Gajah. 2: 27–34. Archived (PDF) from the original on 18 November 2016. Retrieved 18 October 2011.
- ^ Sukumar, R. (July 2006). "A brief review of the status, distribution and biology of wild Asian elephants Elephas maximus". International Zoo Yearbook. 40 (1): 1–8. doi:10.1111/j.1748-1090.2006.00001.x. ISSN 0074-9664. Archived from the original on 18 March 2024. Retrieved 18 March 2024.
- ^ Sukumar, R. (1990). "Ecology of the Asian Elephant in southern India. II. Feeding habits and crop raiding patterns" (PDF). Journal of Tropical Ecology. 6: 33–53. doi:10.1017/S0266467400004004. S2CID 85129439. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 October 2007.
- ^ Pradhan, N. M. B.; Wegge, P.; Moe, S. R.; Shrestha, A. K. (2008). "Feeding ecology of two endangered sympatric megaherbivores: Asian elephant Elephas maximus and greater one-horned rhinoceros Rhinoceros unicornis in lowland Nepal" (PDF). Wildlife Biology. 14: 147–154. doi:10.2981/0909-6396(2008)14[147:FEOTES]2.0.CO;2. S2CID 85964847. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 March 2023. Retrieved 3 January 2023.
- ^ Sach, Fiona; Dierenfeld, Ellen S.; Langley-Evans, Simon C.; Hamilton, Elliott; Murray Lark, R.; Yon, Lisa; Watts, Michael J. (15 May 2020). "Potential bio-indicators for assessment of mineral status in elephants". Scientific Reports. 10 (1): 8032. Bibcode:2020NatSR..10.8032S. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-64780-0. ISSN 2045-2322. PMC 7229182. PMID 32415129.
- ^ Singh, A. P.; Sharma, Ramesh C. (24 September 2001). "Conflicts between linear developments and Asian elephants in sub - Himalayan zone of Uttranchal". Road Ecology Center. Archived from the original on 18 March 2024. Retrieved 18 March 2024.
- ^ McKay, G. M. (1973). "Behavior and ecology of the Asiatic elephant in southeastern Ceylon". Smithsonian Contributions to Zoology. 125 (125): 1–113. doi:10.5479/si.00810282.125. S2CID 128585445.
- ^ Fernando, P.; Lande, R. (2000). "Molecular genetic and behavioral analysis of social organization in the Asian elephant (Elephas maximus)". Behav Ecol Sociobiol. 48 (1): 84–91. Bibcode:2000BEcoS..48...84F. doi:10.1007/s002650000218. S2CID 33707844.
- ^ a b de Silva, S.; Wittemyer, G. (2012). "A Comparison of Social Organization in Asian Elephants and African Savannah Elephants". International Journal of Primatology. 33 (5): 1125–1141. doi:10.1007/s10764-011-9564-1. S2CID 17209753.
- ^ de Silva, S.; Ranjeewa, A. D. G.; Kryazhimskiy, S. (2011). "The dynamics of social networks among female Asian elephants". BMC Ecology. 11 (1): 17. Bibcode:2011BMCE...11...17D. doi:10.1186/1472-6785-11-17. PMC 3199741. PMID 21794147.
- ^ Sukumar, R. (2003). The Living Elephants: Evolutionary Ecology, Behavior, and Conservation. Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 142. ISBN 978-0-19-510778-4.
- ^ Heffner, R.; Heffner, H. (1980). "Hearing in the elephant (Elephas maximus)". Science. 208 (4443): 518–520. Bibcode:1980Sci...208..518H. doi:10.1126/science.7367876. PMID 7367876. Archived from the original on 17 March 2024. Retrieved 27 September 2013.
- ^ Karanth, K. U. & Nichols, J. D. (1998). "Estimation of tiger densities in India using photographic captures and recaptures" (PDF). Ecology. 79 (8): 2852–2862. doi:10.1890/0012-9658(1998)079[2852:EOTDII]2.0.CO;2. JSTOR 176521. Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 August 2017. Retrieved 7 December 2012.
- ^ "Tiger kills mother, baby elephant". Elephant News. 2006. Archived from the original on 14 July 2014.
- ^ "Tiger kills elephant in Corbett Reserve". The Hindu. 29 January 2011. Archived from the original on 8 February 2024. Retrieved 8 February 2024.
- ^ "Kaziranga elephant killed in tiger attack". The Times of India. 22 October 2014. Archived from the original on 8 February 2024. Retrieved 8 February 2024.
- ^ Thuppil, V.; Coss, R. G. (2013). "Wild Asian elephants distinguish aggressive tiger and leopard growls according to perceived danger". Biology Letters. 9 (5): 20130518. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2013.0518. PMC 3971691. PMID 24026347. Archived from the original on 14 July 2014.
- ^ Rasmussen, L. E. L. (1 June 1999). "Evolution of chemical signals in the Asian elephant,Elephas maximus: behavioural and ecological influences". Journal of Biosciences. 24 (2): 241–251. doi:10.1007/BF02941206. ISSN 0973-7138. S2CID 37477741. Archived from the original on 17 March 2024. Retrieved 27 November 2022.
- ^ a b c d e Schulte, Bruce A.; Bagley, Kathryn; Correll, Maureen; Gray, Amy; Heineman, Sarah M.; Loizi, Helen; Malament, Michelle; Scott, Nancy L.; Slade, Barbara E.; Stanley, Lauren; Goodwin, Thomas E.; Rasmussen, L. E. L. (2005). Mason, Robert T.; LeMaster, Michael P.; Müller-Schwarze, Dietland (eds.). "Assessing chemical communication in elephants". Chemical Signals in Vertebrates 10. Boston, MA: Springer US: 140–151. doi:10.1007/0-387-25160-X_18. ISBN 978-0-387-25160-8. Archived from the original on 22 November 2022. Retrieved 27 November 2022.
- ^ Jainudeen, M. R.; McKay, G. M.; Eisenberg, J. F. (1972). "Observation on musth in the domesticated Asiatic elephant (Elephas maximus)". Mammalia. 36 (2): 247–261. doi:10.1515/mamm.1972.36.2.247. S2CID 84275661.
- ^ a b Rasmussen, L.E.L (1 June 2003). "Frontalin: a Chemical Message of Musth in Asian Elephants (elephas maximus)". Chemical Senses. 28 (5): 433–446. doi:10.1093/chemse/28.5.433. PMID 12826539. Archived from the original on 3 November 2022. Retrieved 27 November 2022.
- ^ Brown, J.L.; Schmitt, D.L.; Bellem, A.; Graham, L.H.; Lehnhardt, J. (November 1999). "Hormone Secretion in the Asian Elephant (Elephas maximus): Characterizationof Ovulatory and Anovulatory Luteinizing Hormone Surges". Biology of Reproduction. 61 (5): 1294–1299. doi:10.1095/biolreprod61.5.1294. ISSN 0006-3363. PMID 10529277.
- ^ Rasmussen, L. E. L.; Lee, T. D.; Zhang, A. J.; Roelofs, W. L.; Daves, G. D. (1997). "Purification, identification, concentration and bioactivity of (Z)-7-dodecen-1-yl acetate: sex pheromone of the female Asian elephant, Elephas maximus". Chemical Senses. 22 (4): 417–437. doi:10.1093/chemse/22.4.417. PMID 9279465.
- ^ Rasmussen, L. E. L.; Lee, T. D.; Roelofs, W. L.; Zhang, A. J.; Daves, G. D. (1996). "Insect pheromone in elephants". Nature. 379 (6567): 684. Bibcode:1996Natur.379..684R. doi:10.1038/379684a0. PMID 8602213. S2CID 4330432.
- ^ Rasmussen, L.E.L (22 February 1996). "Insect Pheromones in Elephants" (PDF). Nature. 379 (6567): 684. Bibcode:1996Natur.379..684R. doi:10.1038/379684a0. PMID 8602213. S2CID 4330432. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 November 2022. Retrieved 27 November 2022.
- ^ a b c Schulte, Bruce A.; LaDue, Chase A. (30 September 2021). "The Chemical Ecology of Elephants: 21st Century Additions to Our Understanding and Future Outlooks". Animals. 11 (10): 2860. doi:10.3390/ani11102860. ISSN 2076-2615. PMC 8532676. PMID 34679881.
- ^ Crawley, J. A. H.; Mumby, H. S.; Chapman, S. N.; Lahdenperä, M.; Mar, K. U.; Htut, W.; Thura Soe, A.; Aung, H. H.; Lummaa, V. (5 August 2017). "Is bigger better? The relationship between size and reproduction in female Asian elephants". Journal of Evolutionary Biology. 30 (10): 1836–1845. doi:10.1111/jeb.13143. ISSN 1010-061X. PMID 28703384. Archived from the original on 21 May 2024. Retrieved 21 May 2024.
- ^ Owen-Smith, R. Norman (1988). Megaherbivores: The Influence of Very Large Body Size on Ecology. Cambridge University Press. pp. 145–150. ISBN 978-0-521-42637-4. Archived from the original on 21 May 2024. Retrieved 21 May 2024.
- ^ Johnson, Edward W.; Rasmussen, Lel (1 July 2002). "Morphological characteristics of the vomeronasal organ of the newborn Asian elephant (Elephas maximus)". The Anatomical Record. 267 (3): 252–259. doi:10.1002/ar.10112. ISSN 0003-276X. PMID 12115276. S2CID 30345793.
- ^ "Elephant Social Organisation". ccrsl. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 29 August 2015.
- ^ Fernando, P.; Vijayakrishnan, S.; Ranjeewa, A. D.; Pastorini, J. (2022). "Size-age class scale for Asian elephants". Gajah. 55: 30–39.
- ^ Mumby, H. S.; Chapman, S. N.; Crawley, J. A.; Mar, K. U.; Htut, W.; Thura Soe, A.; Lummaa, V. (2015). "Distinguishing between determinate and indeterminate growth in a long-lived mammal". BMC Evolutionary Biology. 15 (1): 1–9. Bibcode:2015BMCEE..15..214M. doi:10.1186/s12862-015-0487-x. PMC 4604763. PMID 26464339.
- ^ "'Oldest known elephant in captivity' dies at 88 in India". BBC News. 7 February 2019.
- ^ Pacifici, M.; Santini, L.; Di Marco, M.; Baisero, D.; Francucci, L.; Grottolo Marasini, G.; Visconti, P.; Rondinini, C. (2013). "Generation length for mammals". Nature Conservation. 5: 87–94. doi:10.3897/natureconservation.5.5734. Archived from the original on 26 January 2021. Retrieved 20 November 2020.
- ^ Hart, Benjamin L.; Hart, Lynette A.; McCoy, Michael; Sarath, C. R. (November 2001). "Cognitive behaviour in Asian elephants: use and modification of branches for fly switching". Animal Behaviour. 62 (5): 839–847. doi:10.1006/anbe.2001.1815. ISSN 0003-3472. Archived from the original on 5 February 2017. Retrieved 18 March 2024.
- ^ Barrett, Lisa P.; Benson-Amram, Sarah (August 2021). "Multiple assessments of personality and problem-solving performance in captive Asian elephants (Elephas maximus) and African savanna elephants (Loxodonta africana)". Journal of Comparative Psychology. 135 (3): 406–419. doi:10.1037/com0000281. ISSN 1939-2087. PMID 34166041.
- ^ Wikramanayake, E.; Fernando, P.; Leimgruber, P. (2008). "Behavioral response of satellite-collared elephants to the tsunami in southern Sri Lanka". Biotropica. 38 (6): 775–777. doi:10.1111/j.1744-7429.2006.00199.x. S2CID 85358582.
- ^ S., J. K.; Williams, J. H. (October 1950). "Elephant Bill". The Geographical Journal. 116 (4/6): 229. Bibcode:1950GeogJ.116..229S. doi:10.2307/1789395. ISSN 0016-7398. JSTOR 1789395. Archived from the original on 21 May 2024. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ Aldous, P. (2006). "Elephants see themselves in the mirror". New Scientist. Archived from the original on 11 May 2015. Retrieved 24 August 2017.
- ^ Poole, J. (1997). Elephants. World Life Library. p. 61. ISBN 978-0-896-58357-3.
- ^ Sanderson, G. P. (1879). Thirteen years among the wild beasts of India. London: W.H. Allen and Co. p. 80.
- ^ Nissani, M. (2006). "Do Asian elephants apply causal reasoning to tool use tasks?". Journal of Experimental Psychology: Animal Behavior Processes. 31 (1): 91–96. doi:10.1037/0097-7403.32.1.91. PMID 16435969.
- ^ Wang, David Q-H; Carey, Martin C (7 August 2014). "Therapeutic uses of animal biles in traditional Chinese medicine: An ethnopharmacological, biophysical chemical and medicinal review". World Journal of Gastroenterology. 20 (29): 9952–9975. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.9952. ISSN 1007-9327. PMC 4123376. PMID 25110425.
- ^ Nijman, Vincent; Shepherd, Chris R. (12 July 2017). "Ethnozoological assessment of animals used by Mon traditional medicine vendors at Kyaiktiyo, Myanmar". Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 206: 101–106. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2017.05.010. ISSN 0378-8741. PMID 28506903. Archived from the original on 21 May 2024. Retrieved 18 March 2024.
- ^ Lim, Teckwyn; Campos-Arceiz, Ahimsa (2022). "A Review of Human-Elephant Ecological Relations in the Malay Peninsula: Adaptations for Coexistence". Diversity. 14 (1): 36. doi:10.3390/d14010036. ISSN 1424-2818.
- ^ de la Torre, J. A.; Wong, E. P.; Lechner, A. M.; Zulaikha, N.; Zawawi, A.; Abdul-Patah, P.; Saaban, S.; Goossens, B.; Campos-Arceiz, A. (October 2021). "There will be conflict – agricultural landscapes are prime, rather than marginal, habitats for Asian elephants". Animal Conservation. 24 (5): 720–732. Bibcode:2021AnCon..24..720D. doi:10.1111/acv.12668. ISSN 1367-9430. Archived from the original on 18 March 2024. Retrieved 18 March 2024.
- ^ a b c Barua, M. (2010). "Whose issue? Representations of human-elephant conflict in Indian and international media". Science Communication. 32: 55–75. doi:10.1177/1075547009353177. S2CID 143335411. Archived from the original on 8 October 2013. Retrieved 29 January 2012.
- ^ a b Choudhury, A. U. (2004). "Human–Elephant Conflicts in Northeast India" (PDF). Human Dimensions of Wildlife. 9 (4): 261–270. Bibcode:2004HDW.....9..261C. doi:10.1080/10871200490505693. S2CID 145776270. Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 January 2014. Retrieved 27 September 2013.
- ^ Fernando, P. (2000). "Elephants in Sri Lanka: past present and future" (PDF). Loris. 22 (2): 38–44. Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 January 2014. Retrieved 8 December 2012.
- ^ Choudhury, A. U. (2007). "Impact of border fence along India – Bangladesh border on elephant movement" (PDF). Gajah. 26: 27–30. Archived (PDF) from the original on 25 April 2012. Retrieved 18 October 2011.
- ^ Rangarajan, M., Desai, A., Sukumar, R., Easa, P. S., Menon, V., Vincent, S., Ganguly, S., Talukdar, B. K., Singh, B., Mudappa, D., Chowdhary, S., Prasad, A. N. (2010). Gajah: Securing the future for elephants in India Archived 19 June 2013 at the Wayback Machine. Report of the Elephant Task Force. Ministry of Environment and Forests, New Delhi.
- ^ Choudhury, A. (2004). Human–elephant conflicts in Northeast India. Human Dimensions of Wildlife, 9(4), 261–270. doi:10.1080/10871200490505693
- ^ Woodroffe, Rosie; Thirgood, Simon; Rabinowitz, Alan (2005), Rabinowitz, Alan; Woodroffe, Rosie; Thirgood, Simon (eds.), "The impact of human–wildlife conflict on natural systems", People and Wildlife, Conflict or Co-existence?, Conservation Biology, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 1–12, ISBN 978-0-521-82505-4, archived from the original on 18 November 2019, retrieved 19 May 2024
- ^ Bist, S. S. (2006). "Elephant conservation in India – an overview" (PDF). Gajah. 25: 27–35. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 June 2013. Retrieved 30 January 2012.
- ^ Raihan Sarker, A. H. M., & Røskaft, E. (2010). Human–wildlife conflicts and management options in Bangladesh, with special reference to Asian elephants (Elephas maximus). International Journal of Biodiversity Science, Ecosystem Services & Management, 6(3–4), 164–175. doi:10.1080/21513732.2011.554867
- ^ Santiapillai, Charles; Wijeyamohan, S.; Bandara, Ganga; Athurupana, Rukmali; Dissanayake, Naveen; Read, Bruce (12 October 2010). "An assessment of the human-elephant conflict in Sri Lanka". Cey. J. Sci. (Bio. Sci.). 39 (1): 21. doi:10.4038/cjsbs.v39i1.2350.
- ^ Hoare, R. E. (1999). Determinants of human–elephant conflict in a land-use mosaic. Journal of applied ecology, 36(5), 689–700. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2664.1999.00437.x
- ^ Rasmussen, L. E. L. (1999). Evolution of chemical signals in the Asian elephant, Elephas maximus: behavioural and ecological influences. Journal of Biosciences, 24(2), 241–251. doi:10.1007/BF02941206
- ^ Sukumar, R. (1995). Elephant raiders and rogues. Natural History, 104(7), 52–61.
- ^ a b Stiles, D. (2009). The elephant and ivory trade in Thailand. Archived 4 March 2012 at the Wayback Machine TRAFFIC Southeast Asia, Petaling Jaya, Selangor, Malaysia.
- ^ Stiles, D. (2009). "The status of ivory trade in Thailand and Vietnam" (PDF). TRAFFIC Bulletin. 22 (2): 83–91. Archived from the original on 17 April 2019. Retrieved 8 December 2012.
- ^ Flynn, V.; Stewart-Cox, B. & Melidonis, C. (2018). Skinned; The growing appetite for Asian elephants (PDF) (Report). London: Elephant Family. Archived (PDF) from the original on 26 April 2018. Retrieved 26 April 2018.
- ^ Latimer E; Zong JC; Heaggans SY; Richman LK; Hayward GS (2011). "Detection and evaluation of novel herpesviruses in routine and pathological samples from Asian and African elephants: Identification of two new probosciviruses (EEHV5 and EEHV6) and two new gammaherpesviruses (EGHV3B and EGHV5)". Veterinary Microbiology. 147 (1–2): 28–41. doi:10.1016/j.vetmic.2010.05.042. PMC 2976818. PMID 20579821.
- ^ Reid CE, Hildebrandt TB, Marx N, Hunt M, Thy N, Reynes JM, Schaftenaar W, Fickel J (2006). "Endotheliotropic elephant herpes virus (EEHV) infection. The first PCR-confirmed fatal case in Asia". Veterinary Quarterly. 28 (2): 61–64. doi:10.1080/01652176.2006.9695209. PMID 16841568. S2CID 25537428.
- ^ Oo, Zaw Min; Aung, Ye Htut; Aung, Tin Tun; San, Nyo; Tun, Zaw Min; Hayward, Gary S.; Zachariah, Arun (January 2020). "Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus Hemorrhagic Disease in Asian Elephant Calves in Logging Camps, Myanmar". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 26 (1): 63–69. doi:10.3201/eid2601.190159. ISSN 1080-6040. PMC 6924905. PMID 31855135.
- ^ Devkota, R.; Brant, S.V.; Thapa, A.; Loker, E.S. (2014) [Published online 2012]. "Sharing schistosomes: the elephant schistosome Bivitellobilharzia nairi also infects the greater one-horned rhinoceros (Rhinoceros unicornis) in Chitwan National Park, Nepal". Journal of Helminthology. 88 (1): 32–40. doi:10.1017/S0022149X12000697. PMID 23113960. S2CID 7039264. Archived from the original on 6 January 2018. Retrieved 18 March 2024.
- ^ Bowen-Jones, E. & Entwistle, A. (2002). "Identifying appropriate flagship species: The importance of culture and local contexts". Oryx. 36 (2): 189–195. doi:10.1017/S0030605302000261.
- ^ Barua, M.; Tamuly, J. & Ahmed, R.A. (2010). "Mutiny or Clear Sailing? Examining the Role of the Asian Elephant as a Flagship Species". Human Dimensions of Wildlife. 15 (2): 145–160. Bibcode:2010HDW....15..145B. doi:10.1080/10871200903536176. S2CID 143021377. Archived from the original on 8 October 2013. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- ^ Vasudev, D.; Goswami, V.; Srinivas, N.; La Nam Syiem, B.; Sarma, A. (2021). "Identifying important connectivity areas for the wide-ranging Asian elephant across conservation landscapes of Northeast India". Diversity and Distributions. 27 (12): 2510–2523. Bibcode:2021DivDi..27.2510V. doi:10.1111/ddi.13419. JSTOR 48632844. S2CID 244245085.
- ^ Shelden, D. (2020). "World Elephant Day 2020". The Atlantic. Archived from the original on 7 September 2020. Retrieved 6 September 2020.
- ^ Shelden, D. (2020). "OKC Zoo to host 2nd annual Asian Elephant Awareness Month". The City Sentinel. Archived from the original on 26 September 2020. Retrieved 6 September 2020.
- ^ Madhusudan, M.D.; Sharma, Narayan; Raghunath, R.; Baskaran, N.; Bipin, C.M.; Gubbi, Sanjay; Johnsingh, A.J.T.; Kulkarni, Jayant; Kumara, Honnavalli N.; Mehta, Prachi; Pillay, Rajeev; Sukumar, Raman (July 2015). "Distribution, relative abundance, and conservation status of Asian elephants in Karnataka, southern India". Biological Conservation. 187: 34–40. Bibcode:2015BCons.187...34M. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2015.04.003. ISSN 0006-3207. Archived from the original on 21 May 2024. Retrieved 20 May 2024.
- ^ Baskaran, Nagarajan (26 October 2013). "An overview of Asian Elephants in the Western Ghats, southern India: implications for the conservation of Western Ghats ecology". Journal of Threatened Taxa. 5 (14): 4854–4870. doi:10.11609/jott.o3634.4854-70. ISSN 0974-7893. Archived from the original on 21 May 2024. Retrieved 20 May 2024.
- ^ "Project Elephant". Government of India. Archived from the original on 21 May 2024. Retrieved 1 April 2024.
- ^ Bandara, Ranjith; Tisdell, Clem (1 April 2003). "Comparison of rural and urban attitudes to the conservation of Asian elephants in Sri Lanka: empirical evidence". Biological Conservation. 110 (3): 327–342. doi:10.1016/S0006-3207(02)00241-0. ISSN 0006-3207. Archived from the original on 21 May 2024. Retrieved 20 May 2024.
- ^ Jeerawat na Thalang (2020). "It's risky, but elephants are feeling frisky". Bangkok Post. Archived from the original on 2 October 2021. Retrieved 6 September 2020.
- ^ Elephant Conservation Network. Proposed Eastern Extension to Salakpra Wildlife Sanctuary (PDF). The Elephant Conservation Network (Report). Archived (PDF) from the original on 21 September 2020. Retrieved 6 September 2020.
- ^ Parashar, U. (2020). "Assam students, environment activists launch online campaign to stop coal mining in elephant reserve". Hindustan Times. Archived from the original on 29 June 2020. Retrieved 6 September 2020.
- ^ Clubb, R.; Rowcliffe, M.; Lee, P.; Mar, K. U.; Moss, C. & Mason, G. J. (2008). "Compromised Survivorship in Zoo Elephants" (PDF). Science. 322 (5908): 1649. Bibcode:2008Sci...322.1649C. doi:10.1126/science.1164298. hdl:1893/974. PMID 19074339. S2CID 30756352. Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 May 2014. Retrieved 9 December 2012.
- ^ Roocroft, Alan; Oosterhuis, James (December 2000). "Foot Care for Captive Elephants". The Elephant's Foot. pp. 1–5. doi:10.1002/9780470292150.ch5. ISBN 978-0-8138-2820-6. Archived from the original on 21 May 2024. Retrieved 19 May 2024.
- ^ Wiese, R. J. (2000). "Asian elephants are not self-sustaining in North America". Zoo Biology. 19 (5): 299–309. doi:10.1002/1098-2361(2000)19:5<299::AID-ZOO2>3.0.CO;2-Z.
- ^ Saragusty, J.; Hermes, R.; Goritz, F.; Schmitt, D.L. & Hildebrandt, T. B. (2009). "Skewed birth sex ratio and premature mortality in elephants". Animal Reproduction Science. 115 (1–4): 247–254. doi:10.1016/j.anireprosci.2008.10.019. PMID 19058933. Archived from the original on 21 June 2013. Retrieved 9 December 2012.
- ^ "Tourism driving illegal elephant trade in Burma and Thailand – video". The Guardian. 24 July 2012. Archived from the original on 2 December 2016. Retrieved 11 December 2016.
- ^ Hile, J. (2002). "Activists Denounce Thailand's Elephant "Crushing" Ritual". National Geographic Society. Archived from the original on 18 October 2002. Retrieved 1 October 2014.
Just before dawn in the remote highlands of northern Thailand, west of the village Mae Jaem, a four-year-old elephant bellows as seven village men stab nails into her ears and feet. She is tied up and immobilized in a small, wooden cage. Her cries are the only sounds to interrupt the otherwise quiet countryside. The cage is called a "training crush." It's the centerpiece of a centuries-old ritual in northern Thailand designed to domesticate young elephants. In addition to beatings, handlers use sleep-deprivation, hunger, and thirst to "break" the elephants' spirit and make them submissive to their owners.
- ^ Han, Jianghua (3 July 2019). "The Study of Thai Elephant Culture Based on the "Elephant Metaphors" in Thai Idioms". Comparative Literature: East & West. 3 (2): 148–162. doi:10.1080/25723618.2019.1701306. ISSN 2572-3618.
- ^ "Thailand and Laos elephant". South East Asia Globe. 28 February 2022. Archived from the original on 1 October 2023. Retrieved 1 December 2023.
- ^ Sukumar, Raman (26 July 2016). "Iconic Fauna of Heritage Significance in India" (PDF). Indian Journal of History of Science. 51 (2.2). doi:10.16943/ijhs/2016/v51i2.2/48450. ISSN 0019-5235. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 February 2023. Retrieved 21 May 2024.
- ^ Baker, Iljas; Kashio, Masakazu (2002). Giants on Our Hands: Proceedings of the International Workshop on the Domesticated Asian Elephant, Bangkok, Thailand, 5 to 10 February 2001. FAO Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific. ISBN 978-974-90757-1-5. Archived from the original on 21 May 2024. Retrieved 21 May 2024.
- ^ Rangarajan, M. (2001). "The Forest and the Field in Ancient India". India's Wildlife History. Delhi: Permanent Black. pp. 1–10. ISBN 978-8-178-24140-1. Archived from the original on 17 March 2024. Retrieved 19 March 2018.
- ^ Liehrmann, Océane; Crawley, Jennie A. H.; Seltmann, Martin W.; Feillet, Sherine; Nyein, U. Kyaw; Aung, Htoo Htoo; Htut, Win; Lahdenperä, Mirkka; Lansade, Léa; Lummaa, Virpi (29 July 2021). "Handler familiarity helps to improve working performance during novel situations in semi-captive Asian elephants". Scientific Reports. 11 (1): 15480. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-95048-w. ISSN 2045-2322. PMC 8322261. PMID 34326446.
- ^ Winn, P. (2017). "War elephants still exist. But only in one forbidding place". Public Radio International (PRI). Archived from the original on 1 March 2017. Retrieved 1 March 2017.
- ^ a b Rajamangalam), Nīlakaṇṭha (1985). The Elephant-lore of the Hindus: The Elephant-sport (Matanga-lila) of Nilakantha. Motilal Banarsidass Publications. pp. 1-10. ISBN 978-8-12080-005-2.
- ^ Sharma, Jayeeta (August 2011). Empire's Garden: Assam and the Making of India. Duke University Press. p. 25. ISBN 978-0-82235-049-1. Archived from the original on 24 May 2022. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ Upham, E. (1829). The History and Doctrine of Budhism: Popularly Illustrated: with Notices of the Kappooism, Or Demon Worship, and of the Bali, Or Planetary Incantations, of Ceylon. London: R. Ackermann.
- ^ Ling, Trevor (March 1971). "Sinhalese buddhism in regent anthropological writing: Some implications". Religion. 1 (1): 49–59. doi:10.1016/0048-721X(71)90007-8. ISSN 0048-721X. Archived from the original on 15 May 2024. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ "Chinese Zodiac". Warriortours. Archived from the original on 15 September 2018. Retrieved 12 June 2017.
Bibliography
- Deraniyagala, Paulus Edward Pieris (1955). Some Extinct Elephants, Their Relatives, and the Two Living Species. Department of National Museums, Ceylon.
Further reading
- Bandara, Ranjith & Clem Tisdell (2004). "The net benefit of saving the Asian elephant a policy and contingent valuation study" (PDF). Ecological Economics. 48 (1): 93–107. Bibcode:2004EcoEc..48...93B. doi:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2003.01.001.
- Miall, L. C.; Greenwood, F. (1878). Anatomy of the Indian Elephant. London: Macmillan and Co.
External links
- Save Elephant Foundation
- International Elephant Foundation
- ElefantAsia: Protecting the Asian elephant
- Asian Elephants at the Zoological Gardens of the World
- Elephant Information Repository Archived 11 July 2017 at the Wayback Machine
- WWF—Asian elephant species profile
- National Zoo Facts on Asian Elephant and a Webcam of the Asian Elephant exhibit
- Environmental Investigation Agency: Illegal Wildlife Trade : Elephants
- IUCN Red List endangered species
- Asian elephant
- Elephas
- EDGE species
- Endangered animals
- Endangered biota of Asia
- Extant Pliocene first appearances
- Fauna of South Asia
- Fauna of Southeast Asia
- Herbivorous mammals
- Mammals described in 1758
- Mammals of Asia
- National symbols of India
- National symbols of Laos
- National symbols of Thailand
- Pliocene mammals of Asia
- Quaternary animals of Asia
- Species that are or were threatened by habitat fragmentation
- Species that are or were threatened by habitat loss
- Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus





